渲染组件是 React Web 开发领域中的一项非常基础的任务。一种方法是使用 renderToReadableStream 函数将 React 组件渲染为流。
什么是 renderToReadableStream?
React 提供了 renderToReadableStream 方法,用于 React 组件的服务器端渲染。我们可以使用此方法将我们的 React 树作为 HTML 呈现为可读的 Web 流。它使我们能够以流媒体格式传输在线内容,而不是一次创建和分发整个网页。
它是如何工作的?
当我们调用 renderToReadableStream 时,我们传入一个 React 组件,我们希望该组件要呈现为 Web 流。此组件应表示完整的文档,包括 HTML 结构。该函数还接受可选参数,这些参数可用于自定义流的行为。
语法
参数
- reactNode - 它是一个要渲染为HTML的React节点。例如,像 <App /> 这样的 JSX 元素。App 组件应呈现 <html> 标记,因为它是为了表示完整内容而创建的。
- optional - 它是一个带有流选项的对象。
返回值
Promise 由 renderToReadableStream 方法返回。如果 shell 成功呈现,则此 Promise 将解析为包含生成的 HTML 内容的可读 Web 流。如果渲染失败,Promise 将被拒绝,从而为用户提供提供后备 shell 的机会。
例子
示例 - 加载内容
我们可以在 React 中以不同的方式使用 renderToReadableStream 方法 -
流内容 - 为了使我们的网站更加用户友好,我们可以在加载时显示其中的部分内容。
输出
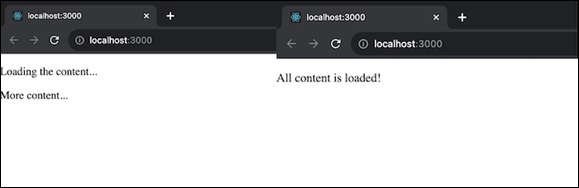
添加自定义脚本 - 我们可以引入自定义脚本来自定义网页显示的行为。
处理错误 - 在显示内容之前,我们可以处理服务器错误,甚至可以更改错误状态代码。
中止渲染 - 我们可以停止服务器渲染,并在必要时让客户端处理其余的渲染。要中止渲染,我们只需根据条件停止渲染内容即可。这是一个简单的例子 -
示例 - 带有帖子的博客应用程序
这个应用程序是一个简单的博客应用程序,显示博客文章列表。每个帖子都有一个标题和内容。BlogApp 组件将一组帖子作为属性,并使用 Post 组件呈现它们。因此,我们将有两个组件:Post 和 BlogApp。帖子组件将显示带有标题和内容的单个博客文章。BlogApp 将是接收一系列帖子并带有标题和内容呈现博客的主要组件。该应用程序将生成一个带有帖子列表的博客。
输出
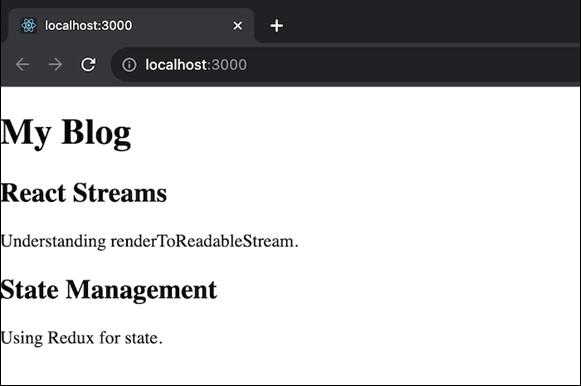
示例 - 电子商务产品目录
在此应用程序中,我们将有一个显示产品列表的电子商务产品目录。每个产品都有名称、价格和描述。ECommerceApp 组件将一系列产品作为属性,并使用 Product 组件呈现它们。我们将有两个组件:Product 和 ECommerceApp。“产品”组件显示具有名称、价格和描述的单个产品。而 ECommerceApp 组件将是获取产品数组并呈现产品目录的主要组件。该应用程序将生成一个包含产品列表的电子商务目录。
输出
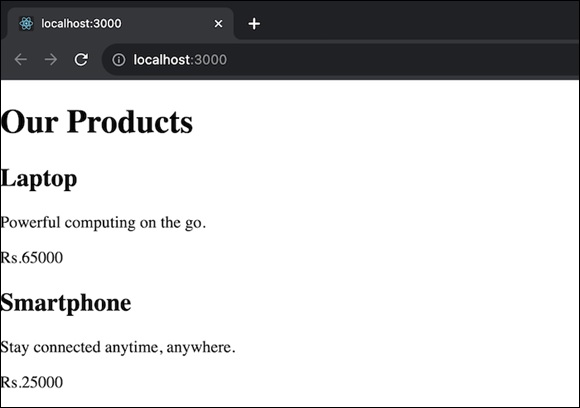
总结
renderToReadableStream 是一种将 React 组件渲染为流的强大方法。它使我们能够创建响应速度更快的应用程序并改善用户体验。



