getChildContext() 函数是 React 中的组件生命周期函数。React 中的这个函数允许父组件与其子组件交换指定信息。它类似于制作一个特定的框(上下文),父级可以在其中存储重要数据。父项确定要放入框中的内容,并允许子项访问它,而无需使用 getChildContext() 直接传递。这种通信方法使事情井井有条,并简化了应用程序的不同部分相互通信的方式,类似于家庭如何以特定的方式讨论关键信息,而无需单独通过每个成员。
语法
为了使用 getChildContext(),组件必须定义一个名为 childContextTypes 的静态属性,该属性指定了预期的上下文数据类型。
例子
示例 1
让我们使用 getChildContext() 函数创建一个示例。在此示例中,我们将创建一个简单的应用程序,该应用程序通过上下文传递用户数据来显示用户信息。
输出
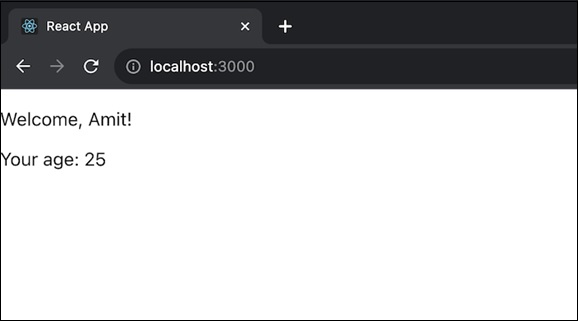
在上面的代码中,App 组件将 UserInfo 组件与 UserProvider 包装在一起,以通过上下文传递用户数据。
示例 2
这是另一个使用 getChildContext() 在 React 应用程序中创建简单主题上下文的示例 -
输出
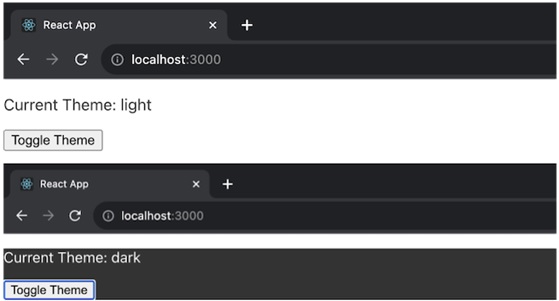
在上面的示例中,ThemeProvider 组件使用 getChildContext() 来提供默认主题为 'light' 的主题上下文和一个用于切换主题的函数。然后,ThemedComponent 使用此上下文来显示有关当前主题和切换按钮的信息。ThemeApp 组件在 ThemeProvider 的上下文中呈现 ThemedComponent。
示例 3
让我们再创建一个示例,使用 getChildContext() 来管理 React 应用程序中的用户身份验证 -
输出
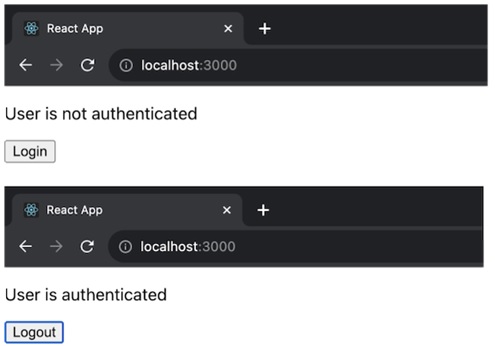
在上面的应用中,AuthProvider 组件使用 getChildContext() 来提供身份验证上下文,并将默认值 isAuthenticated 设置为 false。它还具有管理登录和注销操作的功能。AuthComponent 使用此上下文来查找用户是否已通过身份验证,并提供登录和注销按钮。
局限性
自 React 16.3 起,getChildContext() 函数已被弃用,不鼓励使用其,转而使用新的 Context API。
总结
getChildContext() 函数可用于在 React 组件中提供上下文,建议开发人员采用新的 Context API 以提高可读性和未来的兼容性。



