在 Python 中设置运算符
Python 中的集合运算符是特殊的符号和函数,允许您对集合执行各种操作,例如并集、交集、差集和对称差集。这些运算符提供了一种组合、比较和修改集的方法。
Python 使用以下集合运算符实现它们 -
Python Set 联合运算符 (|)
两个集合的并集是一个包含位于 A 和/或 B 中的所有不同元素的集合。例如
下图说明了两个集的并集。
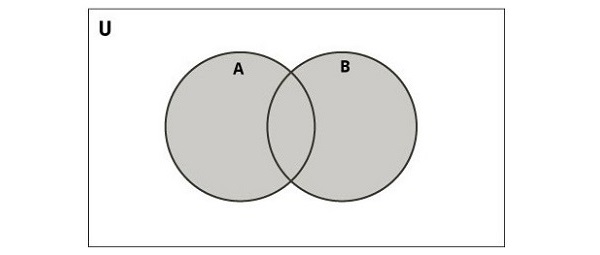
在 Python 中,您可以使用 union() 函数或 | 运算符执行 union 操作。此操作将两个集合的元素组合在一起,同时消除重复项,从而生成一个包含两个集合中所有唯一元素的新集合 -
例以下示例使用 “|” 运算符和 union() 函数,并返回两个集合的并集 −
执行上述代码后,我们得到以下输出 -
The union of set3 and set4 is {73, 6, 8, 9, 45}
Python Set 交集运算符 (&)
两组 AA 和 BB 的交集,用 A∩B 表示,由 A 和 B 中共有的所有元素组成。例如
下图说明了两个集的交集。
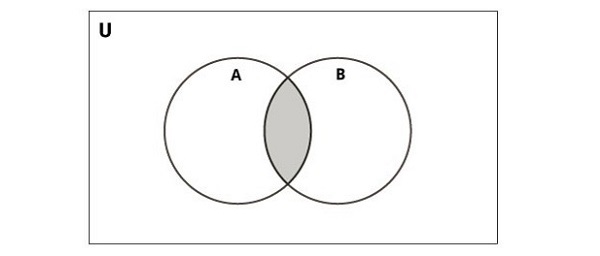
Python提供了 intersection()函数或 & 运算符来执行此操作。结果集仅包含两个集中存在的元素 -
例以下示例使用&运算符和intersection()函数,并返回两个集合的交集 -
它将产生以下输出 -
The intersection of set3 and set4 is {8, 9}
Python 集差集运算符 (-)
两个集合之间的差异(减法)由存在于第一个集合中但不存在于第二个集合中的元素组成。定义如下。集合 A−B 由位于 A 中但不在 B 中的元素组成。例如
下图说明了两组的差异 -
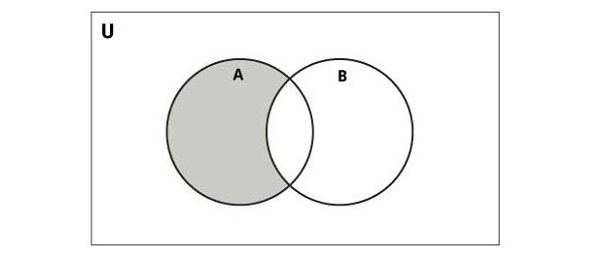
Python 提供了 difference() 函数或 - 运算符来执行此操作。结果集包含第一个集独有的元素 -
例以下示例使用 “-” 运算符和 difference() 函数,并返回两组的差值 -
我们得到的输出如下所示 -
The difference between set3 and set4 is {6}
请注意,“s1-s2” 与 “s2-s1” 不同。
Python Set 对称差分运算符
两个集合的对称差值由存在于任一集合中但不存在于两个集合中的元素组成。A 和 B 的对称差值用 “A Δ B” 表示,由 −
如果 A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} 且 B = {1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9},则 A Δ B = {2, 4, 9}。
下图说明了两组之间的对称差异 -
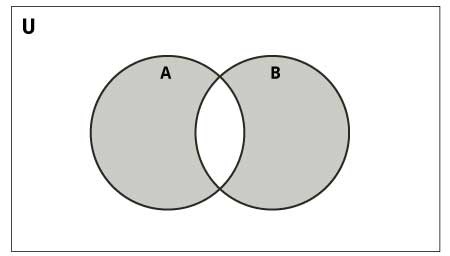
Python 提供了 symmetric_difference() 函数或 ^ 运算符来执行此操作。生成的 set 包含每个 set 唯一的元素。
例以下示例使用 “^” 运算符和 symmetric_difference() 函数,并返回两组的符号差 -
生成的结果如下 -
The symmetric difference of set3 and set4 is {73, 6}
Python 子集测试操作
您可以使用 issubset() 函数或 <= 运算符检查一个集合是否是另一个集合的子集。如果 A 的所有元素也存在于 B 中,则集合 A 被视为另一个集合 B 的子集 -
例以下示例使用 “<=” 运算符和 issubset() 函数,并返回两个集合的子集测试 -
生成的结果如下 -
set3 is a subset of set4: False



