通用网关接口 (CGI) 是一组标准,用于定义如何在 Web 服务器和自定义脚本之间交换信息。CGI 规范目前由 NCSA 维护。
什么是 CGI?
- 通用网关接口 (CGI) 是外部网关程序与信息服务器(如 HTTP 服务器)接口的标准。
- 当前版本为 CGI/1.1,CGI/1.2 正在开发中。
网页浏览
要了解 CGI 的概念,让我们看看当我们单击超链接浏览特定网页或 URL 时会发生什么。
- 您的浏览器联系 HTTP Web 服务器并要求提供 URL,即文件名。
- Web Server 解析 URL 并查找文件名。如果找到该文件,则将其发送回浏览器,否则发送一条错误消息,指示您请求的文件错误。
- Web 浏览器从 Web 服务器获取响应,并显示收到的文件或错误消息。
但是,可以设置 HTTP 服务器,以便在请求某个目录中的文件时不会将该文件发回;相反,它作为一个程序执行,并且该程序输出的任何内容都会发送回给您的浏览器显示。此函数称为公共网关接口或 CGI,程序称为 CGI 脚本。这些 CGI 程序可以是 Python 脚本、PERL 脚本、Shell 脚本、C 或 C++ 程序等。
CGI 架构图
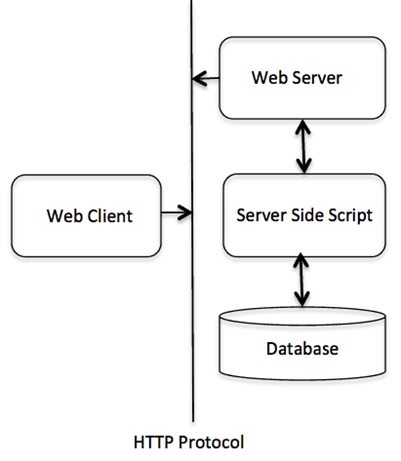
Web 服务器支持和配置
在继续进行 CGI 编程之前,请确保您的 Web 服务器支持 CGI,并且它被配置为处理 CGI 程序。HTTP 服务器要执行的所有 CGI 程序都保存在预配置的目录中。此目录称为 CGI 目录,按照约定,它被命名为 /var/www/cgi-bin。按照惯例,CGI 文件的扩展名为 as。CGI 的 cg,但您也可以保留带有 Python 扩展名 .py 的文件。
默认情况下,Linux 服务器配置为仅运行 /var/www 中 cgi-bin 目录中的脚本。如果要指定任何其他目录来运行 CGI 脚本,请在 httpd.conf 文件中注释以下行 -
<Directory "/var/www/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride None
Options ExecCGI
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
<Directory "/var/www/cgi-bin">
Options All
</Directory>
还应添加以下行,以便 apache 服务器.py文件视为 cgi 脚本。
在这里,我们假设您已经成功启动并运行了 Web Server,并且您能够运行任何其他 CGI 程序,如 Perl 或 Shell 等。
第一个 CGI 程序
这是一个简单的链接,它链接到一个名为 hello.py 的 CGI 脚本。此文件保存在 /var/www/cgi-bin 目录中,其中包含以下内容。在运行 CGI 程序之前,请确保您已使用 chmod 755 hello.py UNIX 命令更改文件模式以使文件可执行。
print ("Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n")
print ('<html>')
print ('<head>')
print ('<title>Hello Word - First CGI Program</title>')
print ('</head>')
print ('<body>')
print ('<h2>Hello Word! This is my first CGI program</h2>')
print ('</body>')
print ('</html>')
注意 − 脚本中的第一行必须是 Python 可执行文件的路径。它在 Python 程序中显示为注释,但它被称为 shebang line。
在 Linux 中,它应该是 #!/usr/bin/python3。
在 Windows 中,它应该是 #!c:/python311/python.exd。
在浏览器中输入以下 URL -
这个 hello.py 脚本是一个简单的 Python 脚本,它将其输出写入 STDOUT 文件,即 screen。有一个重要且额外的功能可用,即要打印的第一行 Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n。此行将发送回浏览器,并指定要在浏览器屏幕上显示的内容类型。
到现在为止,您一定已经了解了 CGI 的基本概念,并且可以使用 Python 编写许多复杂的 CGI 程序。此脚本可以与任何其他外部系统交互,以交换 RDBMS 等信息。
HTTP Header
Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n 行是 HTTP Header的一部分,它被发送到浏览器以理解内容。所有 HTTP Header 都将采用以下格式 -
HTTP Field Name: Field Content
For Example
Content-type: text/html\r\n\r\n
还有一些其他重要的 HTTP Header ,您将在 CGI 编程中经常使用它们。
| Header | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Content-type: |
一个 MIME 字符串,用于定义所返回文件的格式。示例是 Content-type:text/html |
| Expires: Date |
信息失效的日期。浏览器使用它来决定何时需要刷新页面。有效日期字符串的格式为 01 Jan 1998 12:00:00 GMT。 |
| Location: URL |
返回的 URL,而不是请求的 URL。您可以使用此字段将请求重定向到任何文件。 |
| Last-modified: Date |
上次修改资源的日期。 |
| Content-length: N |
返回的数据的长度 (以字节为单位)。浏览器使用此值来报告文件的估计下载时间。 |
| Set-Cookie: String |
设置通过字符串传递的 Cookie |
CGI 环境变量
所有 CGI 程序都可以访问以下环境变量。在编写任何 CGI 程序时,这些变量都起着重要作用。
| 变量名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| CONTENT_TYPE |
内容的数据类型。当客户端将附加内容发送到服务器时使用。例如,文件上传。 |
| CONTENT_LENGTH |
查询信息的长度。它仅适用于 POST 请求。 |
| HTTP_COOKIE |
以键值对的形式返回设置的 cookie。 |
| HTTP_USER_AGENT |
User-Agent request-header 字段包含有关发起请求的用户代理的信息。它是 Web 浏览器的名称。 |
| PATH_INFO |
CGI 脚本的路径。 |
| QUERY_STRING |
通过 GET 方法请求发送的 URL 编码信息。 |
| REMOTE_ADDR |
发出请求的远程主机的 IP 地址。这是有用的日志记录或身份验证。 |
| REMOTE_HOST |
发出请求的主机的完全限定名称。如果此信息不可用,则可以使用 REMOTE_ADDR 获取 IR 地址。 |
| REQUEST_METHOD |
用于发出请求的方法。最常见的方法是 GET 和 POST。 |
| SCRIPT_FILENAME |
CGI 脚本的完整路径。 |
| SCRIPT_NAME |
CGI 脚本的名称。 |
| SERVER_NAME |
服务器的主机名或 IP 地址 |
| SERVER_SOFTWARE |
服务器正在运行的软件的名称和版本。 |
这是一个列出所有 CGI 变量的小 CGI 程序。
import os
print ("Content-type: text/html\r\n\r\n");
print ("<font size=+1>Environment</font><\br>");
for param in os.environ.keys():
print ("<b>%20s</b>: %s<\br>" % (param, os.environ[param]))
GET 和 POST 方法
当您需要将一些信息从浏览器传递到 Web 服务器,并最终传递到 CGI 程序时,您一定遇到过很多情况。最常见的是,浏览器使用两种方法将此信息传递给 Web 服务器。这些方法是 GET Method 和 POST Method。
使用 GET 方法传递信息
GET 方法发送附加到页面请求的编码用户信息。页面和编码信息由 ?字符如下所示 -
- GET 方法是将信息从浏览器传递到 Web 服务器的默认方法,它会生成一个长字符串,该字符串显示在浏览器的 Location:box 中。
- 如果您有密码或其他敏感信息要传递给服务器,切勿使用 GET 方法。
- GET 方法具有大小限制:请求字符串中只能发送 1024 个字符。
- GET 方法使用QUERY_STRING头发送信息,并且可以通过QUERY_STRING环境变量在 CGI 程序中访问。
您可以通过简单地将键和值对与任何 URL 连接起来来传递信息,也可以使用 HTML <FORM> 标签通过 GET 方法传递信息。
简单 URL 示例:Get 方法
这是一个简单的 URL,它使用 GET 方法将两个值传递给 你好_get.py 程序。
下面给出的是 hello_get.py 脚本,用于处理 Web 浏览器给出的输入。我们将使用 cgi 模块,这使得访问传递的信息变得非常容易 -
# Import modules for CGI handling
import cgi, cgitb
# Create instance of FieldStorage
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# Get data from fields
first_name = form.getvalue('first_name')
last_name = form.getvalue('last_name')
print ("Content-type:text/html")
print()
print ("<html>")
print ('<head>')
print ("<title>Hello - Second CGI Program</title>")
print ('</head>')
print ('<body>')
print ("<h2>Hello %s %s</h2>" % (first_name, last_name))
print ('</body>')
print ('</html>')
简单 FORM 示例:GET 方法
此示例使用 HTML FORM 和 submit button 传递两个值。我们使用相同的 CGI 脚本 hello_get.py 来处理这个输入。
<form action = "/cgi-bin/hello_get.py" method = "get">
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "first_name"> <br />
Last Name: <input type = "text" name = "last_name" />
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit" />
</form>
这是上述表格的实际输出,您输入名字和姓氏,然后单击提交按钮查看结果。
使用 POST 方法传递信息
通常,将信息传递给 CGI 程序的更可靠的方法是 POST 方法。这以与 GET 方法完全相同的方式打包信息,但不是将其作为文本字符串发送在 ?在 URL 中,它会将其作为单独的消息发送。此消息以标准输入的形式进入 CGI 脚本。
下面是处理 GET 和 POST 方法的相同 hello_get.py 脚本。
# Import modules for CGI handling
import cgi, cgitb
# Create instance of FieldStorage
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# Get data from fields
first_name = form.getvalue('first_name')
last_name = form.getvalue('last_name')
print "Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n"
print "<html>"
print "<head>"
print "<title>Hello - Second CGI Program</title>"
print "</head>"
print "<body>"
print "<h2>Hello %s %s</h2>" % (first_name, last_name)
print "</body>"
print "</html>"
让我们再举一个与上面相同的示例,它使用 HTML FORM 和 submit button 传递两个值。我们使用相同的 CGI 脚本 hello_get.py 来处理这个输入。
<form action = "/cgi-bin/hello_get.py" method = "post">
First Name: <input type = "text" name = "first_name"><br />
Last Name: <input type = "text" name = "last_name" />
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit" />
</form>
这是上述表单的实际输出。您输入 First 和 Last Name,然后单击 submit 按钮查看结果。
将复选框数据传递给 CGI 程序
当需要选择多个选项时,将使用复选框。
以下是具有两个复选框的表单的示例 HTML 代码 -
<form action = "/cgi-bin/checkbox.cgi" method = "POST" target = "_blank">
<input type = "checkbox" name = "maths" value = "on" /> Maths
<input type = "checkbox" name = "physics" value = "on" /> Physics
<input type = "submit" value = "Select Subject" />
</form>
下面是checkbox.cgi脚本,用于处理 Web 浏览器为复选框按钮提供的输入。
# Import modules for CGI handling
import cgi, cgitb
# Create instance of FieldStorage
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# Get data from fields
if form.getvalue('maths'):
math_flag = "ON"
else:
math_flag = "OFF"
if form.getvalue('physics'):
physics_flag = "ON"
else:
physics_flag = "OFF"
print "Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n"
print "<html>"
print "<head>"
print "<title>Checkbox - Third CGI Program</title>"
print "</head>"
print "<body>"
print "<h2> CheckBox Maths is : %s</h2>" % math_flag
print "<h2> CheckBox Physics is : %s</h2>" % physics_flag
print "</body>"
print "</html>"
将单选按钮数据传递给 CGI 程序
当只需要选择一个选项时,使用 Radio Button。
以下是具有两个单选按钮的表单的示例 HTML 代码 -
<form action = "/cgi-bin/radiobutton.py" method = "post" target = "_blank">
<input type = "radio" name = "subject" value = "maths" /> Maths
<input type = "radio" name = "subject" value = "physics" /> Physics
<input type = "submit" value = "Select Subject" />
</form>
以下是 radiobutton.py 脚本,用于处理 Web 浏览器为单选按钮提供的输入 -
# Import modules for CGI handling
import cgi, cgitb
# Create instance of FieldStorage
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# Get data from fields
if form.getvalue('subject'):
subject = form.getvalue('subject')
else:
subject = "Not set"
print "Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n"
print "<html>"
print "<head>"
print "<title>Radio - Fourth CGI Program</title>"
print "</head>"
print "<body>"
print "<h2> Selected Subject is %s</h2>" % subject
print "</body>"
print "</html>"
将文本区域数据传递到 CGI 程序
当必须将多行文本传递给 CGI 程序时,将使用 TEXTAREA 元素。
以下是带有 TEXTAREA 框的表单的示例 HTML 代码 -
<form action = "/cgi-bin/textarea.py" method = "post" target = "_blank">
<textarea name = "textcontent" cols = "40" rows = "4">
Type your text here...
</textarea>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit" />
</form>
下面是textarea.cgi处理 Web 浏览器提供的输入的脚本 -
# Import modules for CGI handling
import cgi, cgitb
# Create instance of FieldStorage
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# Get data from fields
if form.getvalue('textcontent'):
text_content = form.getvalue('textcontent')
else:
text_content = "Not entered"
print "Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n"
print "<html>"
print "<head>";
print "<title>Text Area - Fifth CGI Program</title>"
print "</head>"
print "<body>"
print "<h2> Entered Text Content is %s</h2>" % text_content
print "</body>"
将下拉框数据传递给 CGI 程序
当我们有许多可用选项但只会选择一个或两个时,会使用下拉框。
以下是带有一个下拉框的表单的示例 HTML 代码 -
<form action = "/cgi-bin/dropdown.py" method = "post" target = "_blank">
<select name = "dropdown">
<option value = "Maths" selected>Maths</option>
<option value = "Physics">Physics</option>
</select>
<input type = "submit" value = "Submit"/>
</form>
下面是 dropdown.py 处理 Web 浏览器提供的输入的脚本。
# Import modules for CGI handling
import cgi, cgitb
# Create instance of FieldStorage
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# Get data from fields
if form.getvalue('dropdown'):
subject = form.getvalue('dropdown')
else:
subject = "Not entered"
print "Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n"
print "<html>"
print "<head>"
print "<title>Dropdown Box - Sixth CGI Program</title>"
print "</head>"
print "<body>"
print "<h2> Selected Subject is %s</h2>" % subject
print "</body>"
print "</html>"
在 CGI 中使用 Cookie
HTTP 协议是一种无状态协议。对于商业网站,需要维护不同页面之间的会话信息。例如,一个用户注册在完成多个页面后结束。如何在所有网页上维护用户的会话信息?
在许多情况下,使用 cookie 是记住和跟踪偏好、购买、佣金以及更好的访问者体验或网站统计数据所需的其他信息的最有效方法。
这个怎么运作?
您的服务器以 cookie 的形式向访问者的浏览器发送一些数据。浏览器可能会接受 cookie。如果是这样,它将作为纯文本记录存储在访客的硬盘驱动器上。现在,当访客到达您网站上的另一个页面时,可以检索 Cookie。检索后,您的服务器知道/记住存储的内容。
Cookie 是 5 个可变长度字段的纯文本数据记录 -
- Expires - Cookie 过期的日期。如果此项为空,则 Cookie 将在访客退出浏览器时过期。
- Domain - 您网站的域名。
- Path - 设置 Cookie 的目录或网页的路径。如果要从任何目录或页面检索 Cookie,则此字段可能为空。
- Secure − 如果此字段包含单词“安全”,则只能使用安全服务器检索 Cookie。如果此字段为空,则不存在此类限制。
- Name = Value − Cookie 以键和值对的形式设置和检索。
设置 Cookie
将 cookie 发送到浏览器非常容易。这些 Cookie 与 HTTP Header一起发送到 Content-type 字段。假设您希望将 UserID 和 Password 设置为 Cookie。设置 Cookie 的执行方式如下 -
print "Set-Cookie:UserID = XYZ;\r\n"
print "Set-Cookie:Password = XYZ123;\r\n"
print "Set-Cookie:Expires = Tuesday, 31-Dec-2007 23:12:40 GMT;\r\n"
print "Set-Cookie:Domain = www.qikepu.com;\r\n"
print "Set-Cookie:Path = /perl;\n"
print "Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n"
...........Rest of the HTML Content....
在此示例中,您必须已了解如何设置 Cookie。我们使用 Set-Cookie HTTP Header 来设置 cookie。
可以选择设置 Cookie 属性,如 Expires、Domain 和 Path。值得注意的是,在发送魔术行 “Content-type:text/html\r\n\r\n.
检索 Cookie
检索所有设置的 cookie 非常容易。Cookie 存储在 CGI 环境变量HTTP_COOKIE中,它们将具有以下形式 -
以下是如何检索 Cookie 的示例。
# Import modules for CGI handling
from os import environ
import cgi, cgitb
if environ.has_key('HTTP_COOKIE'):
for cookie in map(strip, split(environ['HTTP_COOKIE'], ';')):
(key, value ) = split(cookie, '=');
if key == "UserID":
user_id = value
if key == "Password":
password = value
print "User ID = %s" % user_id
print "Password = %s" % password
这将为上述脚本设置的 Cookie 生成以下结果 -
User ID = XYZ
Password = XYZ123文件上传示例
要上传文件,HTML表单必须将enctype属性设置为multipart/form-data。文件类型的 input 标签将创建一个 “Browse” 按钮。
<html>
<body>
<form enctype = "multipart/form-data" action = "save_file.py" method = "post">
<p>File: <input type = "file" name = "filename" /></p>
<p><input type = "submit" value = "Upload" /></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
上面的例子被故意禁用了,以避免人们在我们的服务器上上传文件,但你可以在你的服务器上尝试上面的代码。
以下是处理文件上传的脚本save_file.py -
import cgi, os
import cgitb; cgitb.enable()
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
# Get filename here.
fileitem = form['filename']
# Test if the file was uploaded
if fileitem.filename:
# strip leading path from file name to avoid
# directory traversal attacks
fn = os.path.basename(fileitem.filename)
open('/tmp/' + fn, 'wb').write(fileitem.file.read())
message = 'The file "' + fn + '" was uploaded successfully'
else:
message = 'No file was uploaded'
print """\
Content-Type: text/html\n
<html>
<body>
<p>%s</p>
</body>
</html>
""" % (message,)
如果你在 Unix/Linux 上运行上述脚本,那么你需要注意按如下方式替换文件分隔符,否则在你的 Windows 机器上,上面的 open() 语句应该可以正常工作。
如何引发“文件下载”对话框?
有时,您希望提供用户可以单击链接的选项,它将向用户弹出一个“文件下载”对话框,而不是显示实际内容。这非常简单,可以通过 HTTP Header 实现。此 HTTP Header与上一节中提到的 Header 不同。
例如,如果要使 FileName 文件可从给定链接下载,则其语法如下 -
# HTTP Header
print "Content-Type:application/octet-stream; name = \"FileName\"\r\n";
print "Content-Disposition: attachment; filename = \"FileName\"\r\n\n";
# Actual File Content will go here.
fo = open("foo.txt", "rb")
str = fo.read();
print str
# Close opend file
fo.close()



