Python if else 语句
Python 中的 if-else 语句用于在 if 语句中的条件为 true 时执行一个代码块,当条件为 false 时执行另一个代码块。
if-else 语句的语法
Python 中 if-else 语句的语法如下 -
如果布尔表达式的计算结果为 TRUE,则将执行 if 块内的语句,否则将执行 else 块的语句。
if-else 语句流程图
此流程图显示了如何使用 if-else 语句 -
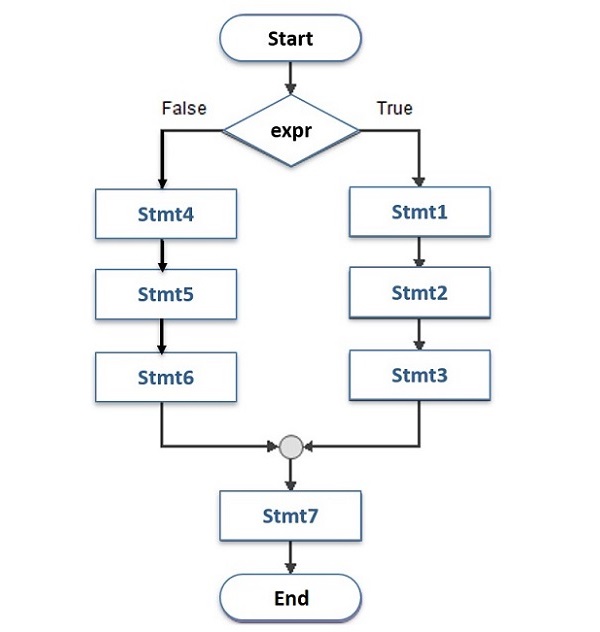
如果 expr 为 True,则执行 stmt1、2、3 的块,然后默认流程继续执行 stmt7。但是,如果 expr 为 False,则阻止 stmt4、5、6 运行,然后默认流继续。
上述流程图的 Python 实现如下 -
Python if-else 语句示例
让我们通过以下示例了解 if-else 语句的用法。在这里,变量 age 可以采用不同的值。如果表达式 age > 18 为 true,则将显示 Eligible to vote 消息,否则将显示 not eligible to vote 消息。以程图说明了此逻辑 -
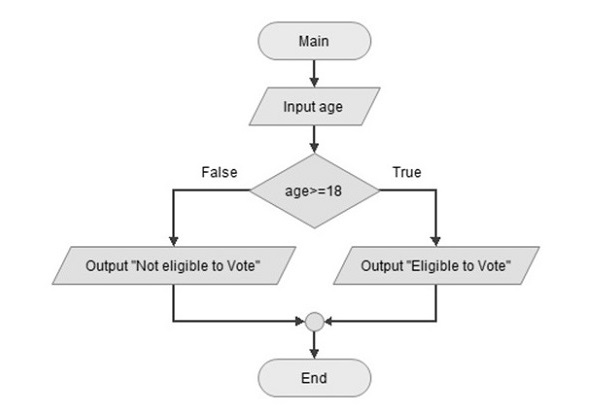
现在,让我们看看上面的流程图 Python 实现。
执行此代码时,您将获得以下输出 -
eligible to vote
要测试 else 块,请将 age 更改为 12,然后再次运行代码。
not eligible to vote
Python if elif else 语句
if elif else 语句允许您检查多个表达式是否为 TRUE,并在其中一个条件的计算结果为 TRUE 时立即执行代码块。
与 else 块类似,elif 块也是可选的。但是,一个程序只能包含一个 else 块,而 if 块后面可以有任意数量的 elif 块。
Python if elif else 语句的语法
如果 elif else Works 如何?
关键字 elif 是 else if 的缩写形式。它允许将逻辑排列在第一个 if 语句之后的 elif 语句级联中。如果第一个 if 语句的计算结果为 false,则后续的 elif 语句将逐个计算,如果满足任何一个语句,则从级联中出来。
级联中的最后一个是 else 块,当所有前面的 if/elif 条件都失败时,它将出现在图片中。
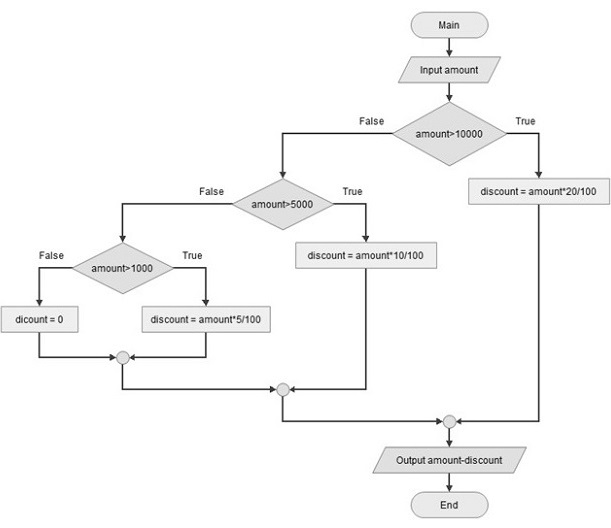
例假设购买时有不同的折扣板 -
- 金额超过 10000 的部分收取 20%的佣金,
- 对于 5-10000 之间的金额,收取 10%,
- 如果介于 1 到 5000 之间,则为 5%。
- 如果金额< 1000,则不享受折扣
以程图说明了这些情况 -
我们可以使用 if-else 语句为上述逻辑编写 Python 代码 -
设置数量以测试所有可能的条件:800、2500、7500 和 15000。输出将相应地变化 -
Payable amount = 800
Amount: 2500
Payable amount = 2375.0
Amount: 7500
Payable amount = 6750.0
Amount: 15000
Payable amount = 12000.0
虽然代码可以正常工作,但如果你查看每个 if 和 else 语句中不断增加的缩进级别,如果还有更多条件,它将变得难以管理。
Python if elif else 语句示例
elif 语句使代码易于阅读和理解。以下是使用 if elif else 语句的相同逻辑的 Python 代码 -
上述代码的输出如下 -
Payable amount = 2375.0



