在 Fetch API 中,Request 接口用于创建资源请求。这是 fetch() 函数以外的另一种创建请求的方法。它还提供了我们可以应用于请求的各种属性和方法。因此,首先,我们将学习 Request() 构造函数,然后如何发送请求,然后是 Request 接口提供的方法和属性。
构造 函数
要创建一个请求对象,我们可以使用 Request() 构造函数和一个 new 关键字。此构造函数包含一个必需参数,该参数是资源的 URL,另一个参数是可选的。
语法
Request() 构造函数具有以下参数 -
- resourceURL - 我们想要获取的资源。其值可以是资源 URL 或 Request 对象。
- Options − 对象 (Object ),它为请求和自定义选项提供其他设置,如下所示 -
- method − 表示 GET、POST、PUT 和 DELETE 等请求方法。
- headers − 为请求设置标头。
- body - 向请求中添加数据。GET 或 HEAD 方法不使用此参数。
- mode − 设置请求的模式,例如 cors、same-origin、no-cors 或 navigate。默认情况下,mode 参数的值为 cors。
- credentials − 它设置要用于请求的凭证,例如 omit、same-origin 或 include。该参数的默认值为 same-origin。
- cache − 设置请求所需的缓存模式。
- redirect − 用于重定向模式,例如 follow、error 或 manual。默认情况下,该参数设置为 follow value。
- referrer − 表示请求的反向链接的字符串,例如 client、URL 或 no-referrer。此参数的默认值是关于客户端的。
- referrerPolicy - 用于设置 referrer 策略。
- integrity - 用于设置给定请求的子资源完整性值。
- keepalive - 用于检查是否为多个请求/响应创建持久连接。
- signal − 表示用于与请求通信或中止请求的 AbortSignal 对象。
- priority - 用于设置请求相对于其他请求的优先级。此参数的可能值为:
- high − 将当前 fetch 请求的优先级设置为高。
- low - 将当前 fetch 请求的优先级设置为低(与其他请求相比)。
- auto − 自动查找当前 fetch 请求的优先级。
发送请求
要发送请求,我们必须首先使用 Request 构造函数创建一个 Request 对象,其中包含其他参数,如 header、body、method、resource URL 等。然后在 fetch() 函数中传递此对象以将请求发送到服务器。现在 fetch() 函数返回一个 promise,该 promise 将使用响应对象进行解析。如果遇到错误,则执行 catch 块。
例
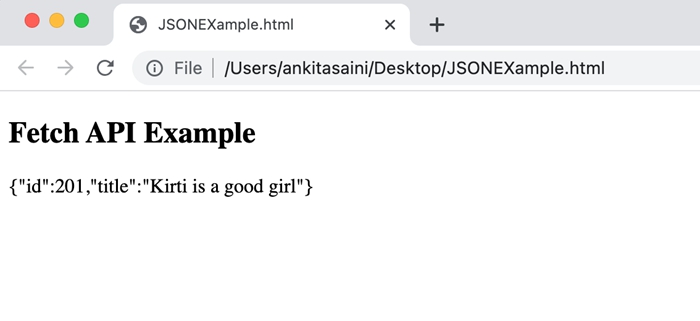
在下面的程序中,我们将创建一个脚本以使用 Request 对象发送数据。因此,为此,我们使用 Request() 构造函数以及 -
- URL – 表示资源 URL。
- method − 这里我们使用 POST 方法,它表示我们正在向服务器发送数据。
- body − 包含我们想要发送的数据。
- header − 表示数据是 JSON 数据。
现在我们在 fetch() 函数中传递请求对象来发送请求并处理服务器返回的响应,并在发生错误时处理错误。
输出
实例属性
请求接口提供的属性是只读属性。所以常用的属性是 -
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Request.url |
此属性包含给定请求的 URL。 |
| Request.body |
此属性包含给定请求的正文。 |
| Request.bodyUsed |
此属性用于判断是否使用请求中存在的正文。其值为 boolean。 |
| Request.destination |
此属性用于告知请求的目的地。 |
| Request.method |
此属性包含 GET、POST、PUT 和 DELETE 等请求方法。 |
| Request.headers |
此属性包含请求的标头对象。 |
| Request.cache |
此属性包含给定请求的缓存模式。 |
| Request.credentials |
此属性包含给定请求的凭据。 |
| Request.mode |
此属性包含给定请求的模式。 |
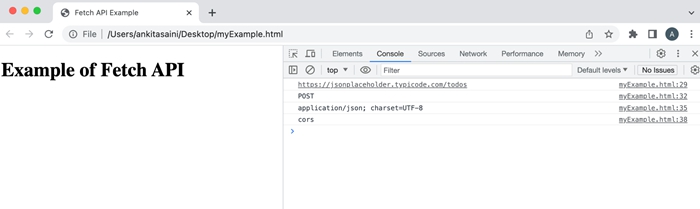
例
在下面的程序中,我们使用 Request 接口提供的属性(如 url、method、headers 和 mode)。
输出
方法
以下是 Request 接口常用的方法 -
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Request.arrayBuffer() |
此方法用于解析请求正文的 ArrayBuffer 表示形式的 Promise。 |
| Request.blob() |
此方法用于解析具有请求正文的 blob 表示形式的 Promise。 |
| Request.clone() |
此方法用于创建当前请求的副本。 |
| Request.json() |
该方法用于将请求体解析为 JSON,并使用解析结果解析 Promise。 |
| Request.text() |
此方法用于解析具有请求正文的文本表示形式的 Promise。 |
| Request.formData() |
此方法用于解析具有请求正文的 formData 表示形式的 Promise。 |
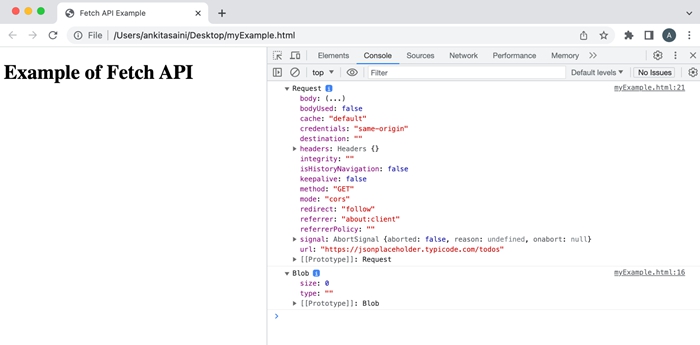
例
在下面的程序中,我们使用了 Request 接口提供的方法(如 blob、clone 等)。
输出
结论
这就是 Request 接口在 Fetch API 中的工作方式。它提供了各种方法来构造和自定义请求。或者我们可以说它提供了灵活性和对请求的更多控制。现在在下一篇文章中,我们将看到 Response 接口在 Fetch API 中的使用。



