图形是一组对象的图形表示形式,其中某些对象对通过链接连接。互连的对象由称为顶点的点表示,连接顶点的链接称为边。与图形相关的各种术语和功能在我们的教程中进行了非常详细的描述。
在本章中,我们将了解如何使用 python 程序创建图形并向其添加各种数据元素。以下是我们对图形执行的基本操作。
- 显示图形顶点
- 显示图形边
- 添加顶点
- 添加边
- 创建图表
可以使用 python 字典数据类型轻松呈现图形。我们将顶点表示为字典中的键,将顶点之间的连接也称为边表示为字典中的值。
请看下面的图表 -
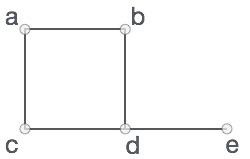
在上图中,
V = {a, b, c, d, e}
E = {ab, ac, bd, cd, de}
E = {ab, ac, bd, cd, de}
例
我们可以在 python 程序中呈现此图,如下所示 -
输出
执行上述代码时,它会产生以下结果 -
{'c': ['a', 'd'], 'a': ['b', 'c'], 'e': ['d'], 'd': ['e'], 'b': ['a', 'd']}
显示图形顶点
为了显示图顶点,我们简单地找到图字典的键。我们使用 keys() 方法。
输出
执行上述代码时,它会产生以下结果 -
['d', 'b', 'e', 'c', 'a']
显示图形边
找到图形边比找到顶点要棘手一些,因为我们必须找到每一对顶点,这些顶点之间有一条边。因此,我们创建一个空的边列表,然后遍历与每个顶点关联的边值。将形成一个列表,其中包含从顶点找到的不同边组。
输出
执行上述代码时,它会产生以下结果 -
[{'b', 'a'}, {'b', 'd'}, {'e', 'd'}, {'a', 'c'}, {'c', 'd'}]
添加顶点
添加顶点很简单,我们可以向图形字典添加另一个额外的键。
例
输出
执行上述代码时,它会产生以下结果 -
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e','f']
添加边
向现有图形添加边涉及将新顶点视为元组并验证边是否已经存在。如果不是,则添加 Edge。
输出
执行上述代码时,它会产生以下结果 -
[{'e', 'd'}, {'b', 'a'}, {'b', 'd'}, {'a', 'c'}, {'a', 'e'}, {'c', 'd'}]



