switch 语句允许根据值列表测试变量是否相等。每个值称为一个 case,并且将针对每个 switch case 检查正在打开的变量。
在 Go 编程中,switch 语句有两种类型 -
- 表达式切换 − 在表达式切换中,个案包含表达式,这些表达式将与 switch 表达式的值进行比较。
- Switch 类型——在 switch 类型中,case 包含与特别注释的 switch 表达式的类型进行比较的类型。
表达式开关
Go 编程语言中表达式 switch 语句的语法如下 -
以下规则适用于 switch 语句 -
- switch 语句中使用的表达式必须具有整型或布尔表达式,或者是类类型,其中类具有到整型或布尔值的单个转换函数。如果未传递表达式,则默认值为 true。
- 一个 switch 中可以有任意数量的 case 语句。每个 case 后跟 to be compare to 的值和一个冒号。
- case 的 constant-expression 必须与 switch 中的变量具有相同的数据类型,并且必须是 constant 或 literals。
- 当被打开的变量等于 case 时,将执行该 case 后面的语句。case 语句中不需要中断。
- switch 语句可以具有可选的 default case,该大小写必须出现在 switch 的末尾。当所有 case 都不为 true 时,默认 case 可用于执行任务。默认情况下不需要中断。
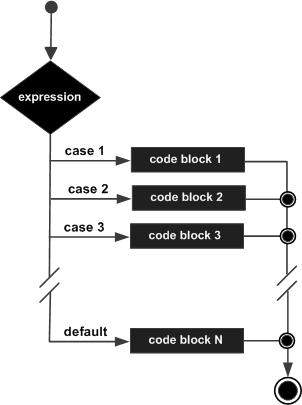
流程图
例
编译并执行上述代码时,它会产生以下结果——
Excellent!
Your grade is A
Your grade is A
类型开关
Go 编程中 type switch 语句的语法如下 -
以下规则适用于 switch 语句 -
- switch 语句中使用的表达式必须具有 interface{} 类型的变量。
- 一个 switch 中可以有任意数量的 case 语句。每个 case 后跟 to be compare to 的值和一个冒号。
- case 的类型必须与 switch 中的变量具有相同的数据类型,并且必须是有效的数据类型。
- 当被打开的变量等于 case 时,将执行该 case 后面的语句。case 语句中不需要中断。
- switch 语句可以具有可选的 default case,该大小写必须出现在 switch 的末尾。当所有 case 都不为 true 时,默认 case 可用于执行任务。默认情况下不需要中断。
例
编译并执行上述代码时,它会产生以下结果——
type of x :<nil>



